
causes of villous atrophy: coeliac (lymphocytic infiltrate), Whipples, dec Ig, lymphoma, trop sprue (rx tetracycline).Ģ9. Diabetes Random >7 or if >6 OGTT (75g) ->11.1 also seen in HCT.Ģ8. insulinoma -> 24 hr supervised fasting hypoglycaemia.Ģ7. diagnosis of polyuria -> water deprivation test, then DDAVP.Ģ6. pemphigus – involves mouth (mucus membranes), pemphigoid – less serious NOT mucosa.Ģ5. severe retroorbital, daily headache, lacrimation -> cluster headache.Ģ4. temporal tenderness-> temporal arteritis -> steroids > 90% ischaemic neuropathy, 10% retinal art occlusion.Ģ3. 1.5 cm difference btwn kidneys -> Renal artery stenosis -> Magnetic resonance angiogram.Ģ2. contraindications lung Surgery -> FEV dec bp 130/90, Ace inhibitors (if proteinuria analgesic induced headache.Ģ1. electrolytes disturbance causing confusion – low/high Na.ġ8. TREMOR postural,slow progression,titubation, relieved by OH->benign essential TREMOR AutDom. sarcoidosis, erythema nodosum, arthropathy -> Loffgrens syndrome benign, no Rx needed.ġ6. middle aged man with KNEE arthritis -> gonococcal sepsis (older people -> Staph).ġ5.

primary hrperparathyroidism -> high Ca, normal/low PO4, normal/high PTH (in elderly).ġ4. Splenectomy -> need pneumococcal vaccine AT LEAST 2 weeks pre-op and for life.ġ3.
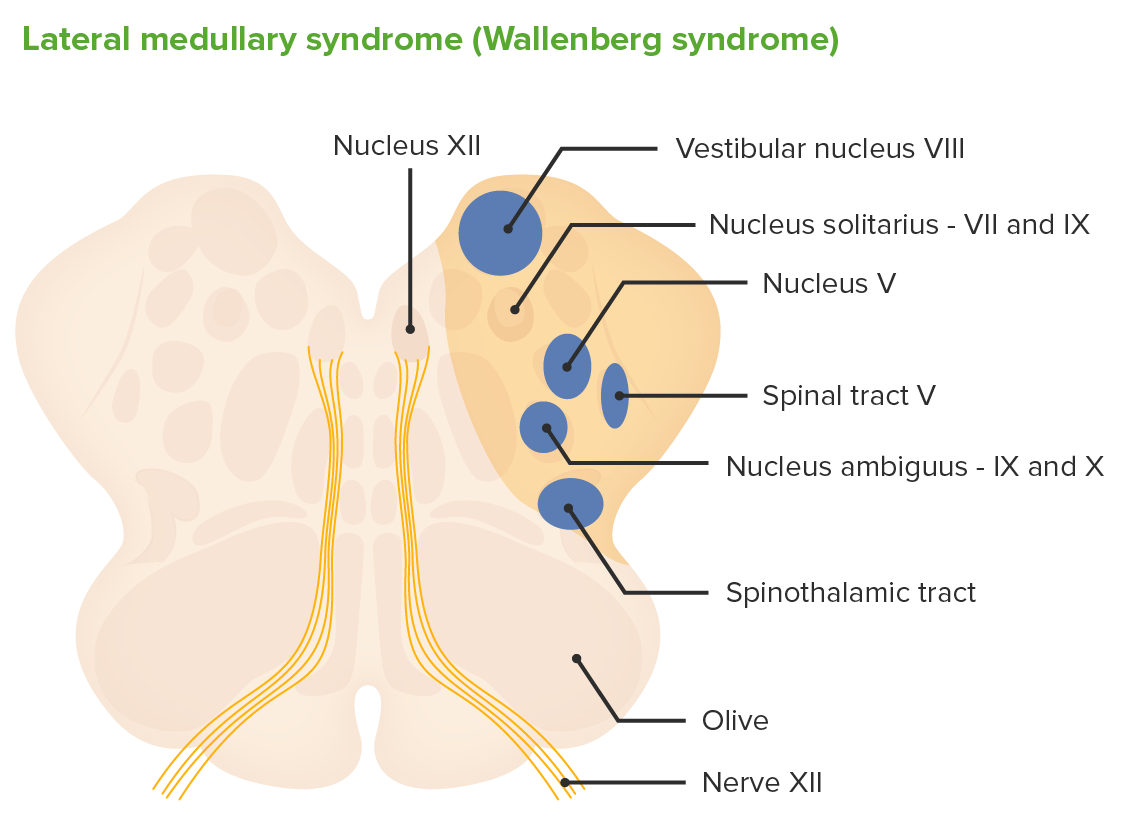
#Wallenburg pica syndrome step 1 skin#
bullae on hands and fragule SKIN torn by minor trauma -> porphyria cutanea tarda.ġ2. cause of gout -> dec urinary excretion.ġ1. foreign travel, macpap rash/flu like illnes -> HIV acute.ġ0. chest discomfort and dysphagia -> achalasia.ĩ. Drug induced pneumonitis -> methotrexate or amiodarone.Ĩ. Obese woman, papilloedema/headache -> Benign Intercanial Hypertention.ħ. Herpes encephalitis -> temporal lobe calicification OR temporoparietal attentuation – subacute onset i.e. Rash on buttocks – Dermatitis herpetiformis (coeliac dx).Ĥ.
#Wallenburg pica syndrome step 1 free#
Cushings – Diagnosis: 24hr urinary free cortisol. Acromegaly – Diagnosis: OGTT followed by GH conc.Ģ. Pulmonary TB is the most common type of TB in persons with HIV infectionĬause of death in AIDS patient or Liver failure is the most common cause of death in people with AIDS)ġ. The most common causes of vision loss affecting patients with AIDS -Cytomegalovirus (CMV) retinitisġ6. Bacillary angiomatosis =cutaneous lesions, which mimic those of Kaposi sarcoma, are the most common manifestationġ5. Acquired most commonly through the mouth or gastrointestinal tractġ4. The most common non-tuberculous mycobacterial infection in AIDS patients is caused by M avium.It is the most common opportunistic infection of bacterial origin in AIDS patients in developed countries. The ileocecal region is the most common site of tuberculosis in the gastrointestinal tractġ3. The liver, spleen, and lymph nodes are the most common sites of extrapulmonary pneumocystosisġ2. Pneumonia is the most common manifestation of P carinii infection in AIDSġ1. Cryptosporidiosis in AIDS=the jejunum is the most common siteġ0. Terminal ileum is the most common gastrointestinal site of disseminated histoplasmosis in the non-AIDS immunocompromised patientĩ. The colon is the most common site of involvement of Histoplasma organisms in he gastrointestinal tract in AIDS patientsĨ. Candidiasis in AIDS=the esophagus is the most common site of infectionħ. Esophagus is the most common site of HIV related ulcerĦ. Cytomegalovirus (CMV), a double-stranded DNA virus in the herpesvirus family, is the mostĬommon cause of life-threatening opportunistic viral infection in AIDS patientsĥ. The most common ocular manifestation of AIDS is a form of retinopathy consisting of cotton-wool spots, hemorrhages, and capillary abnormalities.Ĥ. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is the second most common AIDS-associated neoplasmģ. Kaposi sarcoma is the most common AIDS- related tumor in homosexual men and in populations in parts of AfricaĢ.

CD1a, CD207: Langerhan cell histiocytosis cellsĬD10: Early pre-B cells (immature B cells)ĬD11c, CD25, CD103, CD123: Hairy cell leukemia cellsĬD14, CD64: Monocytic cells (positive in AML-M4 and AML-M5)ĬD23 and CD5 : Chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphomaĬD23 negative and CD5 positive: Mantle cell lymphoma cellsĬD30 positive and CD15 negative: Anaplastic large cell lymphoma cellsĬD31: Endothelial cells (positive in angiosarcoma)ĬD34: Stem cells (also positive in angiosarcoma)ĬD41, CD61: Megakaryocytes and platelets (positive in AML-M7)ĬD45 : All leukocytes (except Reed-Sternberg cells!)ĬD68: Histiocytes (positive in malignant fibrous histiocytosis)ĬD117: Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) cells, mast cells (positive in mastocytosis), myeloid cells


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
